Cisco VRF mit OSPF Routing
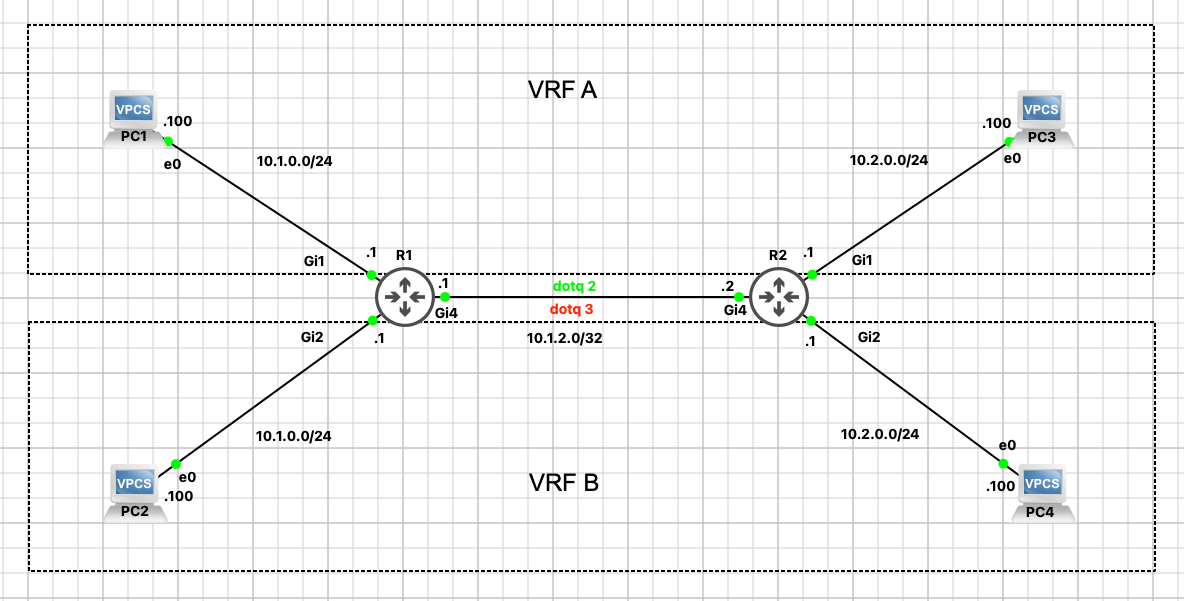
Anlegen von VRFs und das Routing per OSPF v2
Als erstes die Konfiguration der Router
Die PCs haben im entsprechenden Netz immer die .100 als Adresse
Router 1
hostname R1
!
!
ip vrf A
description VRF-A
!
ip vrf B
description VRF-B
!
interface GigabitEthernet1
ip vrf forwarding A
ip address 10.1.0.1 255.255.255.0
negotiation auto
!
interface GigabitEthernet2
ip vrf forwarding B
ip address 10.1.0.1 255.255.255.0
negotiation auto
!
interface GigabitEthernet4
no ip address
negotiation auto
!
Anlegen von Sub Interfacen, damit mehr als ein VRF auf einem Port konfiguriert werden kann.
Das vorgehen ist von „Router on a Stick“ bekannt
!
!
interface GigabitEthernet4.2
encapsulation dot1Q 2
ip vrf forwarding A
ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.252
!
interface GigabitEthernet4.3
encapsulation dot1Q 3
ip vrf forwarding B
ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.252
!
Router 2
hostname R2
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
!
no aaa new-model
!
ip vrf A
description VRF-A
!
ip vrf B
description VRF-B
!
!
interface GigabitEthernet1
ip vrf forwarding A
ip address 10.2.0.1 255.255.255.0
negotiation auto
!
interface GigabitEthernet2
ip vrf forwarding B
ip address 10.2.0.1 255.255.255.0
negotiation auto
!
interface GigabitEthernet4
no ip address
negotiation auto
!
Anlegen der SubInterface
interface GigabitEthernet4.2
encapsulation dot1Q 2
ip vrf forwarding A
ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.252
!
interface GigabitEthernet4.3
encapsulation dot1Q 3
ip vrf forwarding B
ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.252
!
VRF Routing anlegen
Router 1
router ospf 1 vrf A
router-id 1.1.1.1
network 10.1.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 10.1.2.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
!
router ospf 2 vrf B
router-id 1.1.1.1
network 10.1.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 10.1.2.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
!
Router 2
router ospf 1 vrf A
router-id 2.2.2.2
network 10.1.2.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
network 10.2.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
!
router ospf 2 vrf B
router-id 2.2.2.2
network 10.1.2.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
network 10.2.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
!
Alles prüfen
R1#sh ip protocols vrf A
*** IP Routing is NSF aware ***
Routing Protocol is „ospf 1“
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Router ID 1.1.1.1
It is an area border router
Number of areas in this router is 1. 1 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
10.1.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
10.1.2.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
2.2.2.2 110 00:16:51
Distance: (default is 110)
R1#sh ip protocols vrf B
*** IP Routing is NSF aware ***
Routing Protocol is „ospf 2“
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Router ID 1.1.1.1
It is an area border router
Number of areas in this router is 1. 1 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
10.1.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
10.1.2.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
2.2.2.2 110 00:17:18
Distance: (default is 110)
OSPF prüfen
R1#sh ip ospf neighbor
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface
2.2.2.2 1 FULL/DR 00:00:34 10.1.2.2 GigabitEthernet4.3
2.2.2.2 1 FULL/DR 00:00:33 10.1.2.2 GigabitEthernet4.2
Routen prüfen
R1#sh ip route vrf A ospf
Routing Table: A
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 5 subnets, 3 masks
O 10.2.0.0/24 [110/2] via 10.1.2.2, 00:15:20, GigabitEthernet4.2
R1#sh ip route vrf B ospf
Routing Table: B
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 5 subnets, 3 masks
O 10.2.0.0/24 [110/2] via 10.1.2.2, 00:15:51, GigabitEthernet4.3

