Cisco VRF
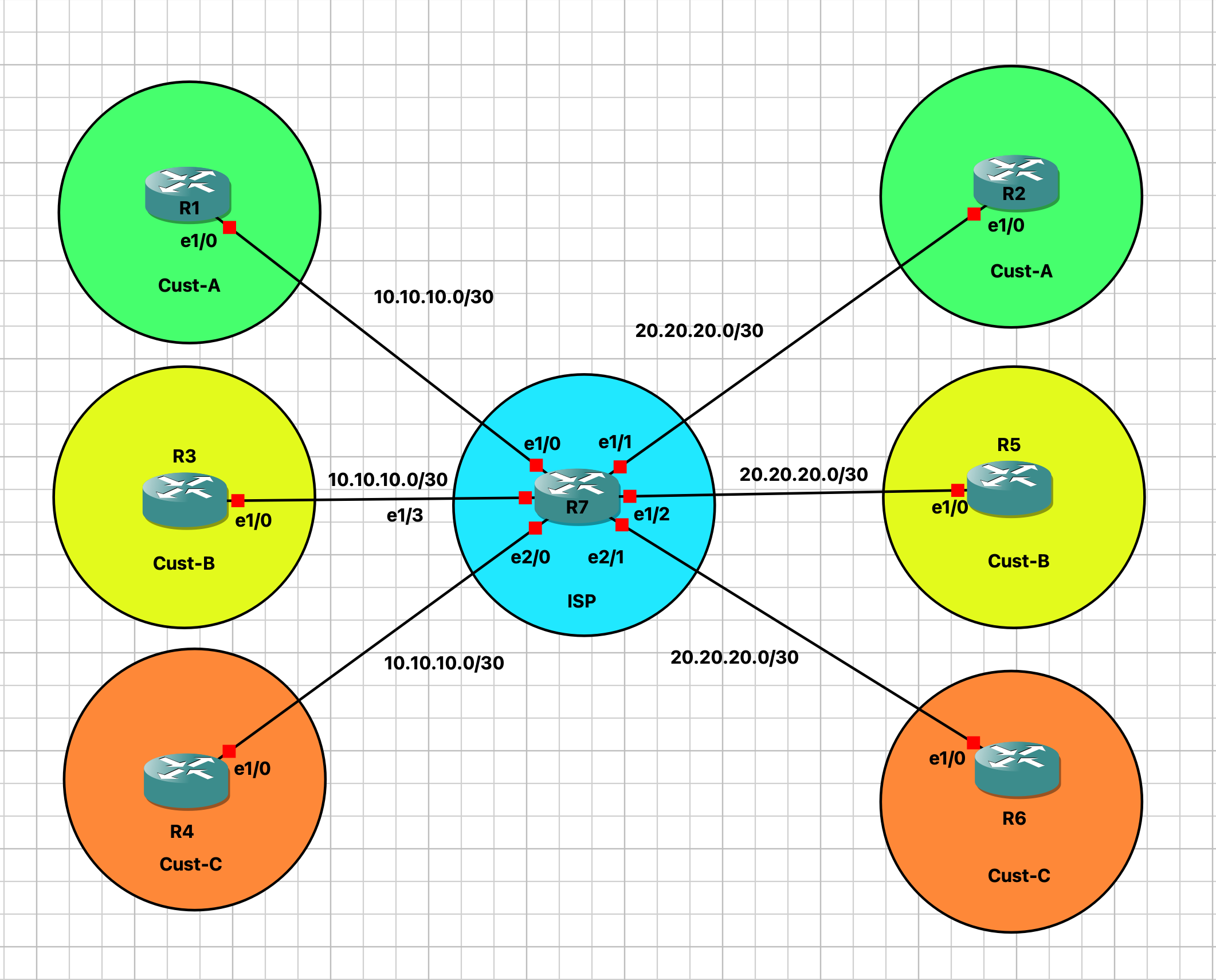
VRF bedeutet Virtual Routing and Forwarding (Cisco Design Guide)
Das heisst im Klartext, das auf einem Router/Layer 3 Switch virtuelle Routinginstanzen angelegt werden können.
Wie im Bild zu sehen ist, werden die selben IP Netze verwendet für unterschiedliche Kunden, was im normalen Fall nicht möglich wäre, lässt sich durch VRFs trennen.
Die Konfiguration der Router
R7 – der Hauptrouter
Anlegen der VRF Instanzen
ip vrf Customer-A
description Customer-A
!
ip vrf Customer-B
description Customer-B
!
ip vrf Customer-C
description Customer-C
!
Interface Konfiguration
interface Ethernet1/0
ip vrf forwarding Customer-A
ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252
half-duplex
!
interface Ethernet1/1
ip vrf forwarding Customer-A
ip address 20.20.20.1 255.255.255.252
half-duplex
!
interface Ethernet1/2
ip vrf forwarding Customer-B
ip address 20.20.20.1 255.255.255.252
half-duplex
!
interface Ethernet1/3
ip vrf forwarding Customer-B
ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252
half-duplex
!
interface Ethernet2/0
ip vrf forwarding Customer-C
ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252
half-duplex
!
interface Ethernet2/1
ip vrf forwarding Customer-C
ip address 20.20.20.1 255.255.255.252
half-duplex
!
Das Routing
router eigrp 100
auto-summary
!
address-family ipv4 vrf Customer-C
network 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.3
network 20.20.20.0 0.0.0.3
no auto-summary
autonomous-system 100
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv4 vrf Customer-B
network 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.3
network 20.20.20.0 0.0.0.3
no auto-summary
autonomous-system 100
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv4 vrf Customer-A
network 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.3
network 20.20.20.0 0.0.0.3
no auto-summary
autonomous-system 100
exit-address-family
!
Customer-A
Router R1 und R2
R1
interface Loopback0
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet1/0
ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.252
half-duplex
!
router eigrp 100
network 1.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.3
no auto-summary
!
R2
interface Loopback0
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet1/0
ip address 20.20.20.2 255.255.255.252
half-duplex
!
router eigrp 100
network 2.2.2.0 0.0.0.255
network 20.20.20.0 0.0.0.3
no auto-summary
!
Customer-B
Router R3 und R5
R3
interface Loopback0
ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet1/0
ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.252
half-duplex
!
router eigrp 100
network 3.3.3.0 0.0.0.255
network 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.3
no auto-summary
!
R5
interface Loopback0
ip address 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet1/0
ip address 20.20.20.2 255.255.255.252
half-duplex
!
router eigrp 100
network 5.5.5.0 0.0.0.255
network 20.20.20.0 0.0.0.3
no auto-summary
!
Customer-C
Router R4 und R6
R4
interface Loopback0
ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet1/0
ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.252
half-duplex
!
router eigrp 100
network 4.4.4.0 0.0.0.255
network 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.3
no auto-summary
!
R6
interface Loopback0
ip address 6.6.6.6 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet1/0
ip address 20.20.20.2 255.255.255.252
half-duplex
!
router eigrp 100
network 6.6.6.0 0.0.0.255
network 20.20.20.0 0.0.0.3
no auto-summary
!
Überprüfung auf R7
Die VRF Instanzen anzeigen
ISP#sh ip vrf
Name Default RD Interfaces
Customer-A Et1/0
Et1/1
Customer-B Et1/2
Et1/3
Customer-C Et2/0
Et2/1
Das Routing
Hier bekommt man keine Anzeige, da alles in virtuellen Instanzen läuft
ISP#sh ip route
Codes: C – connected, S – static, R – RIP, M – mobile, B – BGP
D – EIGRP, EX – EIGRP external, O – OSPF, IA – OSPF inter area
N1 – OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 – OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 – OSPF external type 1, E2 – OSPF external type 2
i – IS-IS, su – IS-IS summary, L1 – IS-IS level-1, L2 – IS-IS level-2
ia – IS-IS inter area, * – candidate default, U – per-user static route
o – ODR, P – periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
Gibt man die VRF Instanz mit an, dann bekommt man die Routing Informationen für genau diese Instanz
ISP#sh ip route vrf Customer-A
Routing Table: Customer-A
Gateway of last resort is not set
1.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 1.1.1.0 [90/409600] via 10.10.10.2, 00:14:05, Ethernet1/0
2.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 2.2.2.0 [90/409600] via 20.20.20.2, 00:14:05, Ethernet1/1
20.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 20.20.20.0 is directly connected, Ethernet1/1
10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 10.10.10.0 is directly connected, Ethernet1/0
ISP#sh ip route vrf Customer-B
Routing Table: Customer-B
Gateway of last resort is not set
3.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 3.3.3.0 [90/409600] via 10.10.10.2, 00:14:09, Ethernet1/3
20.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 20.20.20.0 is directly connected, Ethernet1/2
5.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 5.5.5.0 [90/409600] via 20.20.20.2, 00:14:09, Ethernet1/2
10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 10.10.10.0 is directly connected, Ethernet1/3
ISP#sh ip route vrf Customer-C
Routing Table: Customer-C
Gateway of last resort is not set
4.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 4.4.4.0 [90/409600] via 10.10.10.2, 00:14:13, Ethernet2/0
20.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 20.20.20.0 is directly connected, Ethernet2/1
6.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 6.6.6.0 [90/409600] via 20.20.20.2, 00:14:13, Ethernet2/1
10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 10.10.10.0 is directly connected, Ethernet2/0


